What Happens to Your Body When Gum Infections are Ignored or Left Untreated?
Published Date: October 08, 2024 Last Update: October 08, 2024
Author: Dr. Manpreet S. Walia
Gum infections can seem to be a small issue to some, but can have a serious impact on our oral and overall health if it is ignored and not given importance to. This article shares in detail all about gum infections and its effect on our health including impact on heart, diabetes, etc. Gum infections, also known as periodontal diseases, are more than just a minor dental issue. While many of us might dismiss bleeding gums or occasional tenderness as insignificant, ignoring gum infections can have serious consequences, not just for your oral health but for your entire body. The reality is that untreated gum infections can lead to a cascade of health issues that may affect more than just your mouth.
In this blog, we’ll dive into what happens when gum infections are ignored, the impact they can have on your body, and why it’s so crucial to address them early on.
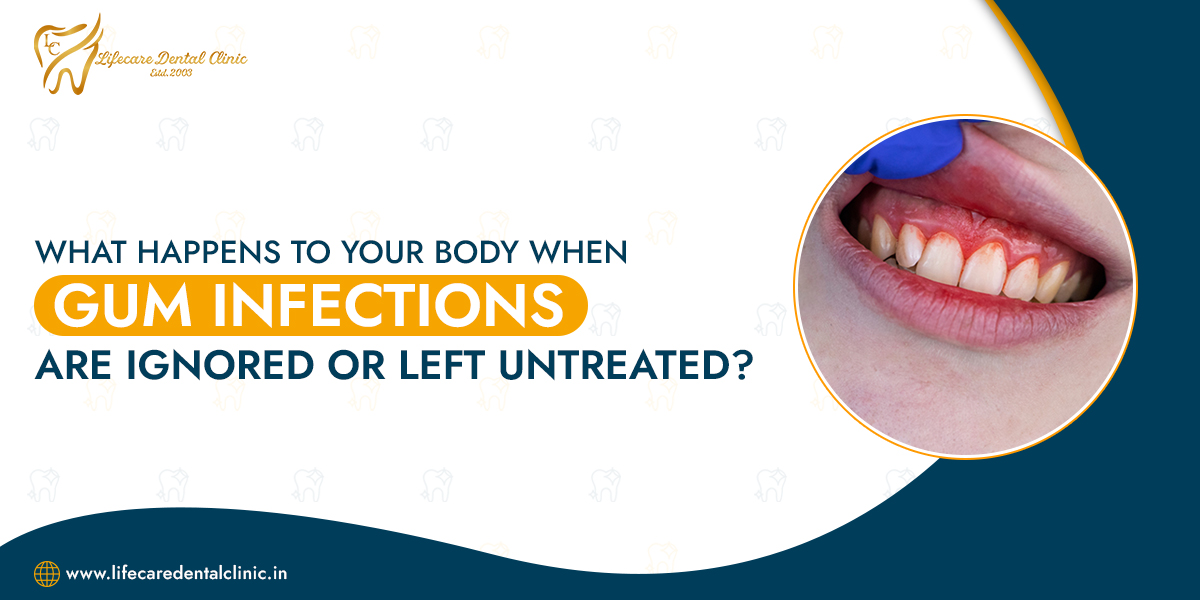
What Are Gum Infections?
Gum infections occur when bacteria in the mouth accumulate on the teeth and gums, leading to inflammation. The early stage of a gum infection is called gingivitis, where the gums become red, swollen, and prone to bleeding. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease where the infection can spread below the gum line and damage the supporting structures of the teeth, including the bone.
The Progression of Gum Infections
Ignoring gum infections doesn’t make them go away and actually get worse with time. Here’s how gum infections typically progress:
1. Gingivitis
This is the early stage of a gum infection, where plaque builds up on the teeth and irritates the gums. At this stage, the infection is reversible with proper oral care and treatment. However, if left untreated, it can progress.
2. Early Periodontitis
As the infection worsens, pockets start to form between the teeth and gums. Bacteria thrive in these pockets, leading to further inflammation and damage.
3. Advanced Periodontitis
At this stage, the infection destroys the bone and connective tissues that hold your teeth in place. Teeth may become loose, and in some cases, tooth loss can occur.
But the damage doesn’t stop in your mouth—gum infections can affect your entire body.
How Gum Infections Impact Your Oral Health
Ignoring gum infections can lead to several oral health problems including:
-
Tooth Loss
One of the most common consequences of untreated gum infections is tooth loss. As the infection destroys the bone and tissue around your teeth, they become loose and may eventually fall out or require extraction.
-
Receding Gums
Gum infections can cause your gums to pull away from your teeth, exposing the roots. This can lead to increased sensitivity and a higher risk of cavities and further infections.
-
Bad Breath
Chronic bad breath, or halitosis, is a common sign of gum infections. The buildup of bacteria and decaying food particles in the gum pockets creates an unpleasant odor that won’t go away with simple brushing or mouthwash.
-
Abscesses
In severe cases, gum infections can lead to painful abscesses—pockets of pus that form in the gums or around the roots of the teeth. These abscesses can be very painful and may require drainage or surgical intervention.
Here’s how gum infections can affect different parts of your body:
1. Heart Disease
One of the most concerning effects of untreated gum infections is the link to cardiovascular disease. The bacteria from gum infections can enter the bloodstream and cause inflammation in the blood vessels, leading to the buildup of plaque in the arteries. This increases the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other heart-related problems.
In fact, people with gum infections are more likely to suffer from heart disease compared to those with healthy gums. The inflammation caused by gum infections can lead to a narrowing of the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis, which is a major risk factor for heart disease.
2. Diabetes
The relationship between gum infections and diabetes is a two-way street. People with diabetes are more prone to developing gum infections because high blood sugar levels provide an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive. On the flip side, gum infections can make it more difficult to control blood sugar levels, leading to complications for those with diabetes.
Gum infections cause inflammation, which can impair the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, making it harder to regulate blood sugar levels. This creates a vicious cycle where both conditions exacerbate each other.
3. Respiratory Issues
Believe it or not, the bacteria in your mouth can make their way into your lungs. When you inhale, the bacteria from an untreated gum infection can be drawn into your respiratory system, leading to infections like pneumonia or exacerbating existing conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
People with gum infections are at a higher risk of developing respiratory infections, especially if their immune system is compromised. This is particularly concerning for the elderly or those with pre-existing lung conditions.
4. Pregnancy Complications
Pregnant women with gum infections are at a higher risk of experiencing complications such as preterm birth and low birth weight. The inflammation and bacteria associated with gum infections can increase levels of prostaglandin, a chemical that can induce labor.
Additionally, studies have shown that women with untreated gum infections are more likely to develop preeclampsia, a potentially dangerous pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure.
How to Prevent Gum Infections
Given the potential consequences of leaving gum infections untreated, prevention is key. Here are some ways to prevent gum infections and maintain healthy gums:
-
Practice Good Oral Hygiene
Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, floss daily, and use an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce the bacteria that cause gum infections.
-
Regular Dental Checkups
Visit your dentist at least twice a year for professional cleanings and checkups. Your dentist can identify early signs of gum infections and treat them before they progress.
-
Quit Smoking
Smoking is one of the leading risk factors for gum infections as the immune system weakens on its account, making it harder for your gums to fight with infections. Quitting smoking can greatly reduce your risk of developing gum infections.
-
Healthy Diet
Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals helps support your immune system and keep your gums healthy. Foods high in vitamin C, like citrus fruits and leafy greens, are particularly beneficial for gum health.
Conclusion
Gum infections should never be ignored or left untreated. What may start as minor gum inflammation can quickly progress into a serious condition that affects not only your oral health but also your overall well-being. From tooth loss to life-threatening diseases like heart disease and diabetes, the potential consequences of untreated gum infections are too significant to ignore. Contact Lifecare Dental Clinic for all your oral health problems today. Call +918591297780 to schedule your appointment.

Leave A Reply